
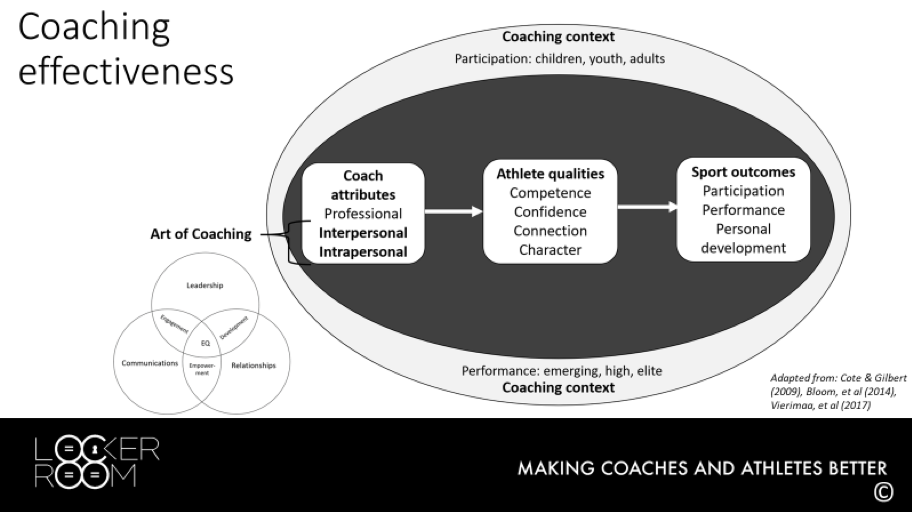
Coaching effectiveness is the application of the coach’s attributes to develop the desired athlete qualities with the objective of achieving sport outcomes across different coaching contexts. One key factor enabling successful outcomes is the quality of the coach-athlete relationship, which is dependent upon among other attributes, the coach’s interpersonal and intrapersonal skills.
Understanding the different personalities, experiences, values and motivations of the diversity of athletes that a coach may interact with provides a starting point for developing quality relationships.
Generation Z (sometimes referred to as Igen) athletes are youth born after 1996. Generation Z (Gen Z) individuals make up 27%, and together with the millennials (those born between 1977 and 1995) 63,5% of the world population. In sub-Saharan Africa, Gen Zs outnumber millennials. It is important to understand the different generations, because they have unique characteristics which have been shaped by social contexts and world events; for example, 9/11, a democratic South Africa, the 2008 financial crisis and most recently the Covid-19 pandemic; occurring during their formative years. Among other factors that have shaped their lives, Gen Zs are the first to grow up in an entirely digital world. They have never known life without computers, mobile phones and the internet!
By being aware of and understanding both the strengths and challenges of Gen Z athletes, coaches will be better prepared to implement effective coaching strategies. However, whilst there are some generalisations across the generation, it is important to recognise that the characteristics certainly do not describe all Gen Z athletes. Cultural contexts should also be considered when considering the influence of your athletes’ characteristics on their behaviours. Understanding each unique athlete is central to enhancing the coach-athlete relationship (even in team sports) and guiding the athlete to attain their own personal potential.
What characterises Gen Z athletes?
Generally, this generation seem to be responsible, compassionate, realistic, open minded, accepting of diversity, curious and open to learning if they understand the “why”. Therefore, coaches should build on these strengths to enhance motivation, satisfaction and commitment. Furthermore, these athletes tend to be visual learners, which provides an opportunity for coaches to incorporate technology into their training sessions to enhance skill development.
The over reliance on technology is a double-edged sword for this generation. Apart from all the advantages of easy access to information, they have shown to be lacking in the ability to distinguish between good and bad information. Constant connection to their phones and the internet is thought to have contributed to shortened attention spans, the ability to focus for only a few minutes and the need for frequent positive feedback. Their preoccupation with social media may be perceived by coaches as distracting, disengaging and time wasting. In addition, as a result of decreased direct contact time, these youth have been found to be prone to depression, anxiety and loneliness, which will have been exacerbated by the Covid-19 lockdowns.
Gen Z athletes tend to have poor communication skills, particularly in person; exhibited by difficulty in communicating verbally, expressing emotions and lacking non-verbal skills such as eye-contact. They prefer impersonal communications such as texting rather than telephone calls or face-to-face conversations.
Other factors that may pose a challenge for coaching these athletes is their lack of a sense of independence and responsibility, together with an over-reliance on parents and coaches. This generation is also perceived to be more entitled, ungrateful and less appreciative than other generations which creates demotivating factors for coaches.
From a sporting performance perspective coaches need to be aware of three characteristics which will impact how they guide Gen Z athletes to develop to their full potential. These athletes are goal directed but tend to focus more on results rather than the training process. Similarly, they tend to be more extrinsically motivated. And there is some evidence that they have poor coping mechanisms to deal with adversity and challenging situations.
How may these characteristics affect how you coach these athletes?
There are many strategies that coaches can implement in their coaching to develop trusting and strong relationships with their Gen Z athletes and tailor training and competition plans for both individual and team players.
The table below provides some ideas for doing this more effectively.
| Coaching Challenges | Suggested strategies | Examples |
| Motivating your athletes for the long-term | Focus on measurable improvement and link training processes to performance outcomes | Set daily process goals and monitor progressEncourage and reinforce hard work that drives their passion |
| Communicating effectively | Use language and tools that enable players to become part of the conversation and provide opportunities for their input and feedback | Seek first to listenAsk open-ended questionsUse texting for logistical arrangements but face-to-face communications for important conversations |
| Working with their attention spans | Be intentional in keeping players engaged and focussedManage distractions to increase attention span | Direct, short and to the point instructions, including team talks – incorporate visual cues and technology where possibleDeliberately create opportunities to increase or decrease distractions as appropriate |
| Setting expectations for practice, behaviour and engagement | Ensure that the athlete(s) clearly understand exactly what is expected of them | Set expectations for cell phone use and then obtain buy-in from the playersModel the behaviours that you expect |
| Creating independent athletes to take ownership | Provide an autonomy- supportive environment that makes athletes accountable | Define the overall structure of the training session, but give players choices, for example, different drills |
| Building resilience to increase confidence | Create challenging scenarios in practice that players may encounter in competition | Provide competition stresses in training and then spend time discussing how the athlete experienced the psychological and emotional stress and what tools (eg breathing exercise) they could use to cope better |
Coaches need to learn and adapt to the generational changes of the athletes they guide by capitalising on their strengths and developing strategies to manage their challenges so that the quality of their relationships with their athletes are enhanced.
To learn more about coach athlete relationships, register for our Creating Congruent Coach-Athlete Relationships Course.
Other courses that you may be interested in:
- Coaching with Emotional Intelligence
- Communicating for Mutual Understanding
References:
- Gould, D., Nalepa, J., & Mignano, M. (2020). Coaching generation Z athletes. Journal of Applied Sport Psychology, 32(1), 104-120.
- Miller, L., & Lu, W. (2018). Gen Z Is Set to Outnumber Millennials Within a Year. Retrieved from https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2018-08-20/gen-z-to-outnumber-millennials-within-a-year-demographic-trends/
- Seemiller, C., & Grace, M. (2016). Generation Z goes to college: John Wiley & Sons.
- Twenge, J. M. (2017). iGen: Why today’s super-connected kids are growing up less rebellious, more tolerant, less happy–and completely unprepared for adulthood–and what that means for the rest of us: Simon and Schuster.
- Wood, J. (2018). Generation Z will outnumber Millennials this year. Retrieved from https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2018/08/generation-z-will-outnumber-millennials-by-2019/
